For a decade, NASA’s NEOWISE spacecraft has been a silent sentinel, tirelessly scanning the celestial expanse for near-Earth objects (NEOs)—asteroids and comets that could potentially pose a threat to our planet.
This remarkable mission, reborn from the ashes of another, has not only provided a treasure trove of data for astronomers but also played a crucial role in planetary defense efforts, becoming an integral part of a vast detection and tracking network.
From WISE to NEOWISE: A Phoenix Rising from Cryogenic Slumber
NEOWISE’s story begins in 2009 with the launch of the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE). This infrared telescope embarked on a groundbreaking mission to survey the entire cosmos in a new light, peering into the depths of space to observe the faint glow of distant galaxies, the comparatively cool embers of red dwarf stars, the explosive death throes of white dwarfs, and the icy tails of comets streaming away from the Sun’s heat. However, WISE’s journey wasn’t meant to last forever. After its cryogenic coolant ran out, hindering its ability to observe the universe’s coldest objects, WISE entered a period of hibernation in 2011.
But the story doesn’t end there. Recognizing the potential of the spacecraft’s remaining capabilities, astronomers, led by the visionary Dr. Amy Mainzer, proposed a clever repurposing. NEOWISE, as the reborn spacecraft was christened, would leverage its unique infrared vision to keep a watchful eye on NEOs. This decision extended the life of a spacecraft initially designed for a mere seven-month mission, transforming it into a decade-long guardian.
A Decade of Discovery: Unveiling a Hidden Population in Our Cosmic Backyard
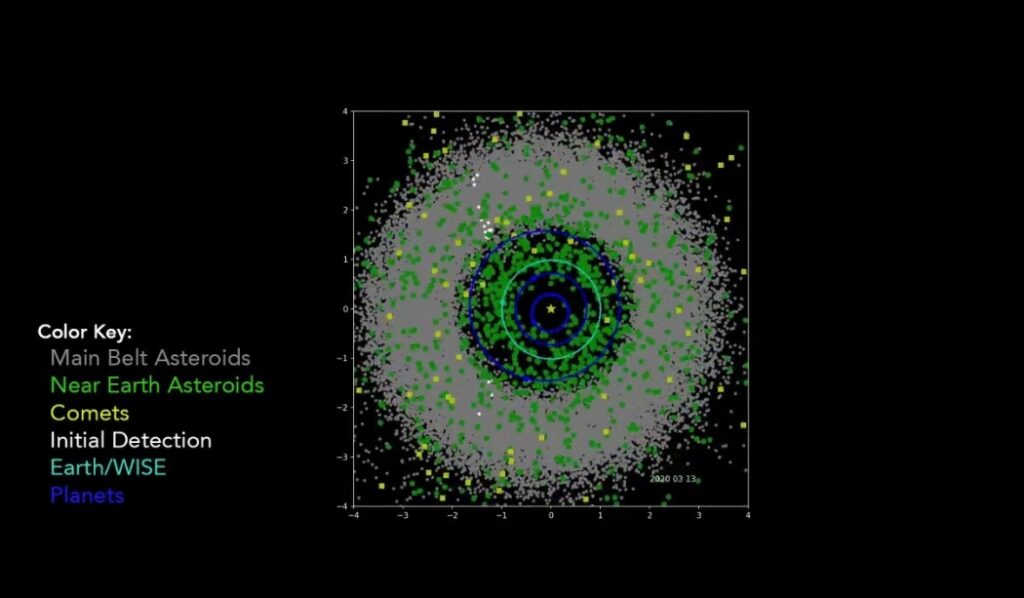
NEOWISE’s keen infrared vision proved to be a powerful tool for a new mission. Unlike telescopes that rely on visible light, NEOWISE could detect the faint heat signature of asteroids and comets, even those veiled in darkness or shrouded in dust. By repeatedly scanning the skies from its low-Earth orbit, it has amassed an impressive collection of data – 1.45 million infrared measurements of over 44,000 solar system objects, including a staggering 3,000 NEOs. This represents a significant contribution to our understanding of these celestial nomads, revealing a hidden population previously unknown. Among these discoveries are 215 previously unidentified NEOs and 25 comets, including the now-famous comet NEOWISE, which captivated skywatchers in 2020 with its greenish glow.
This data has been instrumental in refining the orbits of known NEOs and estimating their sizes, crucial information for assessing any potential threats. The case of Apophis, a potentially hazardous asteroid with a close encounter predicted for 2029, exemplifies NEOWISE’s contribution. By providing more accurate data on Apophis’s trajectory, NEOWISE has helped to rule out the possibility of a collision and alleviate any public concerns.
A Legacy of Data and Discovery: Fueling the Future of Planetary Defense
NEOWISE’s impact extends far beyond its own observations. The data it has collected is freely available to the scientific community, serving as a springboard for further discoveries. Astronomers can use this treasure trove to study how celestial objects change over time, delve into the mysteries of variable stars that pulsate in brightness, and even peer into the fiery hearts of black holes as they devour matter. NEOWISE has become an essential resource for time-domain astronomy, a field that explores the dynamic nature of the universe.
The mission doesn’t operate in isolation. NEOWISE seamlessly integrates with a well-oiled planetary defense network. Every three days, it transmits its observations to the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS), a constellation of communication satellites that act as celestial mail carriers, beaming the data down to Earth. The data is then relayed to IPAC, the astronomical data research center at Caltech. Here, the raw data is transformed into calibrated images and NEO detections, readily accessible to scientists worldwide. This global collaboration allows for rapid identification and characterization of newfound NEOs.
The Future of Planetary Defense: Passing the Torch to the Next Generation
While NEOWISE’s time as a guardian nears its end due to increasing solar activity, its legacy will live on. The data it has collected will continue to fuel scientific exploration for years to come, serving as a foundation for future studies of NEOs and the broader solar system. Additionally, NEOWISE serves as a crucial stepping stone for the next generation of space-based NEO hunters – NASA’s upcoming NEO Surveyor mission.
Scheduled for launch in 2027, this next-gen telescope will carry the torch, focusing on even more elusive NEOs, particularly those that are faint in visible light but radiate brightly in the infrared spectrum, thanks to its advanced sensors and imaging capabilities. With its cutting-edge technology, NEO Surveyor will further our understanding of these celestial objects, helping to refine risk assessments and inform strategies for planetary defense. By building upon NEOWISE’s legacy, NEO Surveyor represents a vital continuation of humanity’s efforts to safeguard our planet and explore the mysteries of the cosmos. As we bid farewell to NEOWISE, we eagerly anticipate the groundbreaking discoveries and insights that lie ahead with the launch of NEO Surveyor.



















