Groundbreaking data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is providing a fresh perspective on the universe’s expansion rate. By utilizing its powerful infrared capabilities, JWST has measured distances to ten nearby galaxies with unprecedented accuracy. Using three independent methods—including Cepheid variable stars, red giants, and carbon stars—researchers have derived a new reading of the universe’s expansion rate, hovering around 70 kilometers per second per megaparsec (km/s/Mpc). This value closely aligns with the 67 km/s/Mpc suggested by cosmic microwave background (CMB) data, potentially bridging the gap between previously conflicting measurements and offering a resolution to the Hubble tension.
For decades, astronomers have debated the rate at which the universe is expanding—a measurement known as the Hubble constant. This debate, known as the “Hubble tension,” arises from discrepancies between methods that observe the CMB, a snapshot of the early universe, and those that measure the expansion of nearby galaxies. The long-standing tension between these methods has led some scientists to question whether something fundamental is missing from our understanding of the universe’s evolution. The new JWST data brings hope that this mystery may finally be solved.
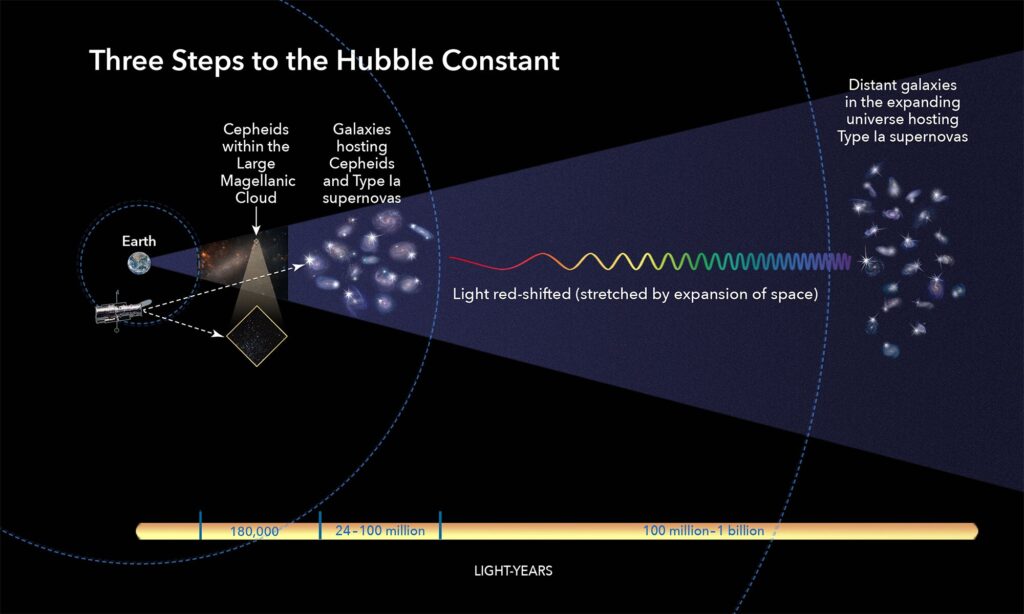
The Hubble tension, which has persisted for years, presents a key challenge in modern cosmology. One of the major methods of measuring the Hubble constant involves the study of the CMB, radiation left over from the Big Bang. By analyzing the CMB, astronomers have calculated an expansion rate of about 67 km/s/Mpc. However, when observing nearby galaxies, the rate jumps to roughly 73 km/s/Mpc. This difference may seem small, but its implications are vast: if true, it could point to new physics beyond the standard model of cosmology.
The JWST’s new data, led by University of Chicago cosmologist Wendy Freedman and her team, challenges the idea that new physics is necessary to explain the Hubble tension. Instead, the results suggest that earlier measurements might have been influenced by systematic errors, particularly in the method involving Cepheid variable stars. Cepheids are highly luminous stars that pulsate in brightness, allowing astronomers to calculate their distance from Earth based on their light. However, Cepheids often exist in crowded regions of galaxies, leading to difficulties in accurately measuring their brightness.
Freedman’s team turned to other methods to cross-check their results, including the use of red giant stars and carbon stars. These stars are not as affected by stellar crowding and dust, which can skew Cepheid measurements. Remarkably, the measurements using these stars produced results that closely aligned with those derived from the CMB, lending support to the idea that the expansion rate of the universe is closer to 70 km/s/Mpc, not 73.
Resolving the Hubble tension is not just about numbers—it’s about our fundamental understanding of the universe. If the JWST’s findings hold, it may suggest that the universe has been expanding uniformly and predictably since the Big Bang. This would reaffirm the standard model of cosmology, which explains the evolution of the universe with known forces like gravity and dark energy. On the other hand, if the tension persists, it might indicate that something deeper is at play, possibly requiring revisions to our understanding of physics, including concepts like dark matter or new particles.
While the results are promising, they are not the final word. Scientists will continue to refine these measurements and expand their analysis to more galaxies. As astronomer Adam Riess points out, although the JWST has confirmed many of Hubble’s measurements, the puzzle of the Hubble tension may still hold surprises.



















