A Rare Celestial Event: The Blaze Star Returns
Astronomy lovers and casual sky gazers alike are in for a treat—T Coronae Borealis (T CrB), also known as the “Blaze Star,” is poised to light up the night sky in a once-in-a-lifetime nova event. This celestial occurrence, predicted to happen before September 2024, will mark the first time the star erupts in over 80 years. What makes this phenomenon even more exciting is that it will be visible to the naked eye, making it accessible for anyone willing to gaze up at the stars.
Understanding the Nova Phenomenon
Novas, particularly recurring ones like T CrB, are the result of an intricate cosmic dance between two stars. In this case, T CrB is a binary star system consisting of a red giant and a white dwarf, orbiting each other every 228 days. The white dwarf, an Earth-sized remnant of a once massive star, is in the process of siphoning hydrogen from its companion red giant. Over time, this stolen hydrogen accumulates on the surface of the white dwarf, creating immense heat and pressure. Once the temperature reaches a staggering 10 million degrees Celsius, a runaway thermonuclear reaction occurs, igniting the nova.
This process is akin to a cosmic clock, ticking down with each passing second until the conditions are just right for an explosion. Historically, T CrB has erupted roughly every 80 years, with the last explosion observed in 1946. This ticking clock nature, combined with modern observational technologies, means that astronomers have a front-row seat to study this event in unprecedented detail.
Why This Nova Is Special
T CrB isn’t just any nova. It’s a recurring nova, one of only ten known in the Milky Way, and it has been studied extensively for centuries. Its eruptions were documented as early as 1866, and the forthcoming explosion will be its first since the advent of modern technology. This allows astronomers to gather invaluable data, offering insights into the physics of stellar evolution and binary star interactions.
Furthermore, this particular explosion is unique because of its proximity—T CrB is situated about 3,000 light years away in the constellation Corona Borealis, making it relatively close on an astronomical scale. This proximity means that when the explosion occurs, the brightness will be significant enough to be seen with the naked eye, even from urban areas with light pollution.
For a few days, the white dwarf will transform into one of the brightest stars in the sky, providing a rare visual spectacle for stargazers.
What sets T CrB apart from many other stellar events is its predictability. While many novae occur sporadically and unpredictably, T CrB’s periodic eruptions give astronomers a unique opportunity to plan and prepare for detailed observations across various wavelengths, including X-rays, visible light, and radio waves.
This will allow researchers to study the nova’s progression in real-time, unlocking secrets about how these explosions evolve and their impact on surrounding space.
The Science Behind the Blaze Star
As hydrogen from the red giant accumulates on the white dwarf’s surface, the increased pressure and temperature set the stage for a thermonuclear reaction. This reaction is similar in nature to the explosion of a hydrogen bomb, albeit on a much larger and more energetic scale.
When the nova occurs, it’s not the white dwarf itself that explodes, but rather the hydrogen that has accumulated on its surface. This material is ejected into space at high speeds, forming a glowing cloud of gas and dust. The remaining white dwarf, having shed its outer layer of hydrogen, resets the clock for the next eruption. Over the following decades, it will once again begin the slow process of siphoning hydrogen from its red giant companion, starting the cycle anew.
This process is crucial for understanding stellar evolution, especially in binary systems. White dwarfs, which are the remnants of stars that have exhausted their nuclear fuel, typically fade away into obscurity. However, in binary systems like T CrB, the interaction between the two stars can reignite the white dwarf, creating a nova that is not only visually spectacular but scientifically enlightening.
Why This Event Matters
The significance of T CrB’s upcoming nova goes beyond its visual appeal. For scientists, this event offers a rare chance to observe and study the dynamics of nova explosions in real-time. While the explosion itself will be short-lived—lasting only a few days—the data gathered during this period will be studied for years to come.
One of the key aspects researchers are eager to investigate is the structure of the accretion disk—the rotating disk of material that forms around the white dwarf as it siphons hydrogen from the red giant.
Moreover, the ability to observe the nova in various wavelengths across the electromagnetic spectrum will provide a comprehensive view of the explosion’s energy output. This multi-wavelength approach allows scientists to examine everything from the heat generated by the explosion to the particles that are accelerated during the event.
How to Witness the Event
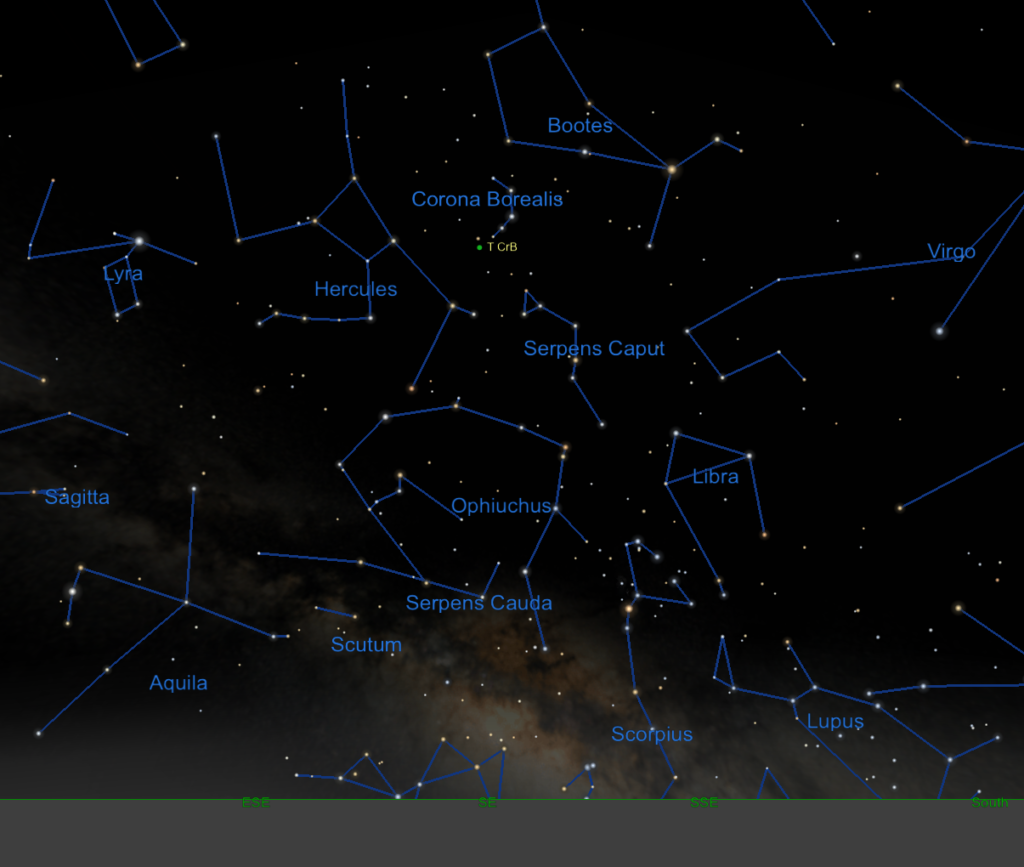
The star is located in the constellation Corona Borealis, also known as the Northern Crown. This small but distinct constellation lies to the west of the more prominent Hercules constellation and above the well-known Big Dipper.
To locate T CrB, stargazers should look for a semi-circle of stars that form the shape of a crown. The nova will appear in this constellation, and during the explosion, it will briefly become one of the brightest stars in the sky, shining with a magnitude of 2 or 3. While the exact timing of the explosion is uncertain, astronomers are confident it will occur before the end of September 2024.
For optimal viewing, it’s best to find a location with minimal light pollution and a clear view of the northern sky. Even if you’re unable to catch the nova at its peak, the entire event will last for several days, providing multiple opportunities to witness this incredible celestial display.
Keep in mind that while the brightest part of the explosion may only last a few hours, the star will remain visible for several days as it slowly fades back into obscurity.
The Broader Impact of T Coronae Borealis
T Coronae Borealis’ nova is more than just a visual spectacle—it’s a reminder of the ever-evolving nature of our universe. These recurring novae offer a unique window into the processes that govern stellar life cycles and the interactions between stars in binary systems. For astronomers, each nova provides critical data that helps refine our understanding of these cosmic events, while for the rest of us, it’s an opportunity to reflect on the vastness and beauty of the cosmos.
This event is a rare convergence of beauty and science. Not only will we be treated to a dazzling display in the night sky, but we will also be participating—simply by looking up—in a moment of astronomical discovery. By observing this nova, we can connect with the same sense of wonder that has inspired humanity’s gaze toward the stars for millennia.
Don’t Miss This Once-in-a-Lifetime Event
In a world where much of the cosmos seems out of reach, T Coronae Borealis’ nova explosion brings the wonders of the universe directly to us. Whether you’re an avid astronomer or someone who simply enjoys marveling at the night sky, this event is not to be missed. The opportunity to witness such a rare explosion, which won’t happen again for another 80 years, is a true gift.
So, mark your calendars, find a spot with a clear view of the northern sky, and prepare to be awed by the brilliance of T Coronae Borealis as it lights up the heavens. In a world full of constant noise and distraction, let this celestial event serve as a reminder of the vast and timeless forces that shape our universe—forces that, for a brief moment, we can see with our own eyes.
Remember, the night sky has always held the power to inspire, and this year, it will do so once again with the fiery return of the Blaze Star. Don’t miss it!
Reference:
“Recurrent Novae and Their Outbursts: A Review of the Physics and Observational History” Authors: Schaefer, B. E., & Patterson, J. Journal: Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 33, Pages 25-64 (2020). DOI: 10.1146/annurev.astro.33.1.25



















