For over 800 years, SN 1181, a supernova that lit up the sky in the year 1181 AD, remained an enigma to astronomers. Historical records from Chinese and Japanese astronomers describe the appearance of this “guest star,” which shone brightly for 185 days near the constellation Cassiopeia. However, the remnants of this cosmic event have only recently been pinpointed, thanks to advanced astronomical techniques and historical research. The remnants are now linked to a rare type of supernova, resulting in the formation of a “zombie star,” defying our understanding of stellar death.
At the heart of this discovery lies an unusual celestial body—a white dwarf that survived the violent explosion of two colliding stars. This collision, which occurred 10,900 years ago, created an incomplete thermonuclear explosion, categorized as a Type Iax supernova. Unlike typical supernovae that obliterate everything in their wake, this event left behind a “zombie star”—a still-burning remnant surrounded by a vast nebula of gas and dust. What makes this star truly fascinating is that it continues to emit stellar wind, something astronomers did not expect to see.
Researchers using the European Space Agency’s XMM-Newton telescope and NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory observed two distinct shock regions in the nebula: an outer shock caused by the initial explosion and a more recent inner shock that points to ongoing stellar activity. This led to the unexpected discovery of stellar wind emanating from the zombie star’s surface. Remarkably, this high-speed wind only began within the past 30 years, long after the supernova explosion.
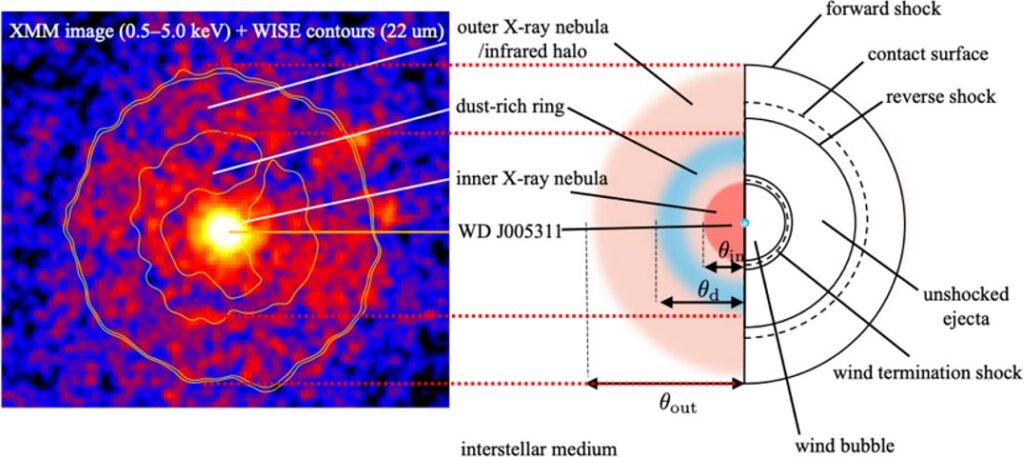
The discovery of SN 1181 and its zombie star offers a rare opportunity to study an event that bridges history and modern astrophysics. The white dwarf at the center of this nebula is one of the hottest in the Milky Way, reaching temperatures of over 200,000 degrees Celsius. This star, surrounded by a nebula 16 light-years wide, provides a unique laboratory for understanding the life cycles of stars and the role they play in creating the elements essential to planetary formation.
Scientists believe studying SN 1181 could unlock answers about how elements heavier than iron, such as those found on Earth, are formed during these rare Type Iax supernovae. The event also underscores the importance of combining ancient observational records with modern technology to deepen our understanding of the cosmos.
Astronomers aren’t done with SN 1181 yet. Ongoing and future studies using the Very Large Array radio telescopes and the Subaru Telescope aim to uncover even more secrets of this ancient supernova remnant. These investigations could shed light on the peculiar nature of Type Iax supernovae and help astronomers refine models of stellar evolution.