Citizen science has taken a giant leap forward in our understanding of the universe! Let’s delve deeper into this groundbreaking mission and explore the secrets it has unlocked.
A collaborative project called “GALAXY CRUISE” has yielded a treasure trove of cosmic discoveries, thanks to the tireless efforts of citizen scientists and the remarkable power of artificial intelligence (AI).
A Universe of Data: The Challenge of Classification
Imagine sifting through a mountain of astronomical data, searching for hidden galaxies amongst a sea of celestial information. This was the daunting task faced by the 10,000 citizen scientists who volunteered their time and expertise for the GALAXY CRUISE project. The project utilized data collected by the Subaru telescope, a marvel of modern astronomy perched atop a dormant volcano in Hawaii. The Subaru telescope’s keen eye captures incredible detail about the cosmos, but this detail comes at a cost – a massive amount of data to be analyzed.
Even with a dedicated army of citizen scientists, classifying the countless galaxies within the dataset was a slow and laborious process. The sheer number of galaxies threatened to turn this ambitious project into a never-ending celestial sorting exercise. This is where AI stepped in, providing a powerful solution to overcome this challenge.
AI to the Rescue: Accelerating Discovery
The research team ingeniously trained AI on a database of galaxies previously classified by human astronomers. This training essentially equipped the AI with the knowledge and expertise required to identify different galaxy types. Imagine a student diligently studying a star chart, learning to distinguish spirals from ellipticals and irregulars. The AI underwent a similar learning process, but at an unimaginable speed. Once armed with this knowledge, the AI was unleashed on the remaining galaxies within the Subaru Telescope data, analyzing them with remarkable speed and accuracy.
The inclusion of AI significantly accelerated the pace of discovery, allowing the project to reach its full potential. However, the true scientific windfall from GALAXY CRUISE lies not just in the sheer number of new galaxies discovered, but in the specific types of galaxies identified.
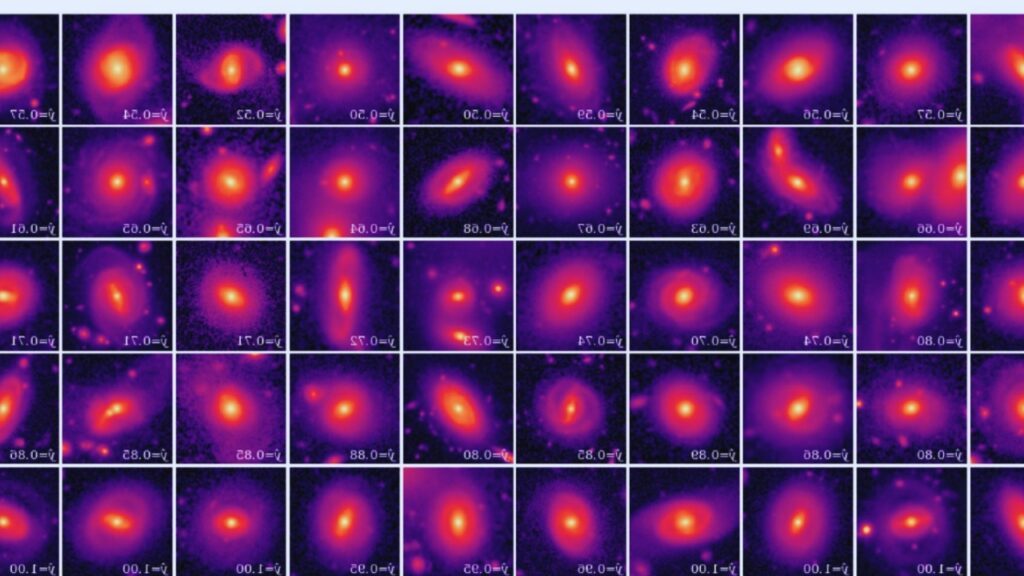
Unveiling a Trove of Rare Ring Galaxies
One of the most significant outcomes of the GALAXY CRUISE project is the discovery of a staggering 30,000 ring galaxies. These celestial objects are unlike any other. Imagine a swirling disc of stars, like our Milky Way, but instead of majestic spiral arms, a prominent ring of brilliant young stars encircles a dense core of ancient stars. Their unique structure has long captivated astronomers, but due to their rarity, relatively few ring galaxies were known to exist.
Prior to GALAXY CRUISE, estimates suggested that ring galaxies comprised only 1% to 3% of all observable galaxies. They were considered cosmic oddities, fleeting glimpses into the diversity of galactic forms. However, the sheer number of ring galaxies unearthed by this project paints a very different picture. With 30,000 newfound ring galaxies added to the celestial map, scientists now have a goldmine of data to analyze.
This unprecedented sample size will allow researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries surrounding ring galaxy formation. Were they forged in the violent collision of two spiral galaxies, a celestial dance that disrupts the usual order and throws stars into a breathtaking ring? Or perhaps some other, as-yet-unknown, mechanism is at play? The wealth of data from GALAXY CRUISE can now be used to test these hypotheses and potentially reveal entirely new formation processes.
A Collaboration for the Cosmos: The Power of Citizen Science and AI
The GALAXY CRUISE project serves as a shining example of the power of collaboration. By combining the tireless efforts of citizen scientists with the analytical prowess of AI, researchers have unveiled a hidden population of galaxies, forever changing our understanding of the cosmos. This discovery is a testament to the boundless potential of human curiosity and ingenuity. It also highlights the transformative potential of citizen science initiatives, where ordinary people with a passion for astronomy can contribute meaningfully to scientific advancement.
The success of GALAXY CRUISE paves the way for even more groundbreaking astronomical achievements in the years to come. As technology continues to evolve and citizen science initiatives gain momentum, we can expect even more remarkable discoveries to illuminate the vast and mysterious universe. Imagine future projects that combine the power of AI with an even larger pool of citizen scientists, delving deeper into astronomical data and unraveling even more cosmic secrets. The future of space exploration is bright, and GALAXY CRUISE is a beacon, lighting the way for a new era of discovery.


















