This year, skywatchers around the world have a rare treat in store. A spectacular “nova” explosion is expected to take place by September in the constellation Corona Borealis, also known as the Northern Crown. This celestial fireworks display, visible to the naked eye despite being 3,000 light-years away, promises to be a once-in-a-lifetime experience.
The Cosmic Culprit: T Coronae Borealis
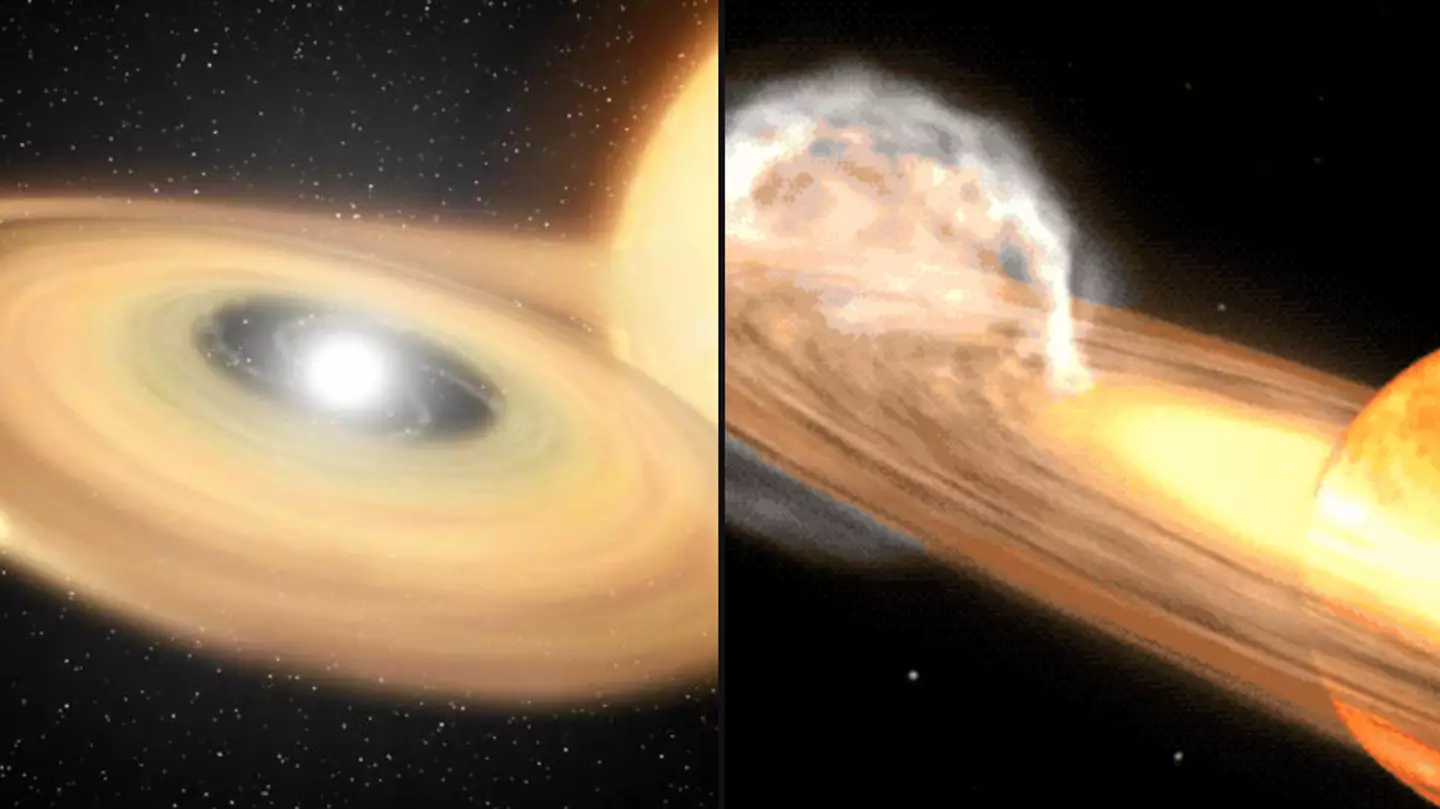
The star system T Coronae Borealis (T CrB) is the mastermind behind this stellar light show. Here, a fascinating cosmic ballet unfolds between a red giant star and a white dwarf – the collapsed core of a once-massive star. The red giant, nearing the end of its stellar life, struggles with increasing internal pressure and temperature. This instability causes it to shed its outer layers of gas and dust, like a colossal peeling onion.
In close proximity orbits the white dwarf, a stellar relic with immense density. With its powerful gravity, the white dwarf starts accreting, or pulling in, this stellar material from its red giant companion. As the material piles up on the white dwarf’s surface, it triggers a dramatic rise in temperature and pressure. This builds towards a critical point where the accreted hydrogen undergoes a runaway thermonuclear reaction, igniting the brilliant nova we’ll witness from Earth.
Nova: A Stellar Snapshot in Time
Veteran skywatchers might recognize the term “nova” from astronomical lore. These outbursts are indeed stellar explosions, but far less energetic than supernovas that mark the complete collapse and death of massive stars. Novae, often compared to colossal hydrogen bombs, are caused by a thermonuclear ignition event on the surface of a white dwarf. The key difference lies in the fuel source. Supernovae arise from the thermonuclear detonation of the collapsing star’s core, whereas novae erupt due to the ignition of accreted material on the white dwarf’s surface.
A Celestial Spectacle Awaits
For those eager to witness this cosmic spectacle, NASA suggests looking towards Corona Borealis, a small, faint constellation located near Bootes and Hercules. The constellation resembles a faint, asymmetrical crown, with the nova expected to appear as a new bright star within its boundaries. At its peak, the nova is expected to rival the North Star in brightness, offering stunning naked-eye views for several days. Binoculars can extend the viewing window to over a week, allowing you to witness the nova’s gradual decline in brilliance.
This phenomenal event is not just a captivating display of celestial fireworks; it’s a valuable scientific opportunity. By studying the properties of the nova’s light and ejecta, astronomers can gain valuable insights into the evolution of binary star systems, the thermonuclear processes at play on white dwarfs, and the chemical composition of stellar material. It’s a chance to witness stellar drama firsthand and expand our understanding of the universe’s dynamic processes.
So, mark your calendars, astronomy enthusiasts! Look towards Corona Borealis this September, and be prepared to be dazzled by a celestial explosion unlike any other. It’s a rare opportunity to witness the raw power and beauty of the cosmos unfolding before your very eyes.
Don’t forget to share your observations with fellow skywatchers and astronomy communities online. By contributing your data, you can help expand our collective knowledge of this fascinating stellar phenomenon.


















