For decades, the icy moons of Jupiter and Saturn, Europa and Enceladus, have captivated scientists searching for extraterrestrial life.
These celestial bodies harbor vast, subsurface oceans, potentially holding the key to unlock the existence of microbial life beyond Earth. However, the immense distance and the icy shells encasing these oceans pose a significant challenge – how do we detect life from millions of miles away, shrouded beneath layers of ice? A recent study published in Science Advances offers a groundbreaking proposition, suggesting that a single grain of ice ejected from these moons could hold the key to unraveling this cosmic mystery.
A World of Potential: Icy Moons and the Allure of Extraterrestrial Life
Europa and Enceladus have emerged as frontrunners in the ongoing quest for extraterrestrial life. Beneath their seemingly barren surfaces lie vast oceans, potentially harboring liquid water – a critical ingredient for life as we know it. Additionally, ongoing evidence of hydrothermal activity on these moons suggests the presence of essential elements and energy sources that could fuel biological processes. However, directly accessing these hidden oceans for analysis presents a formidable technological hurdle.
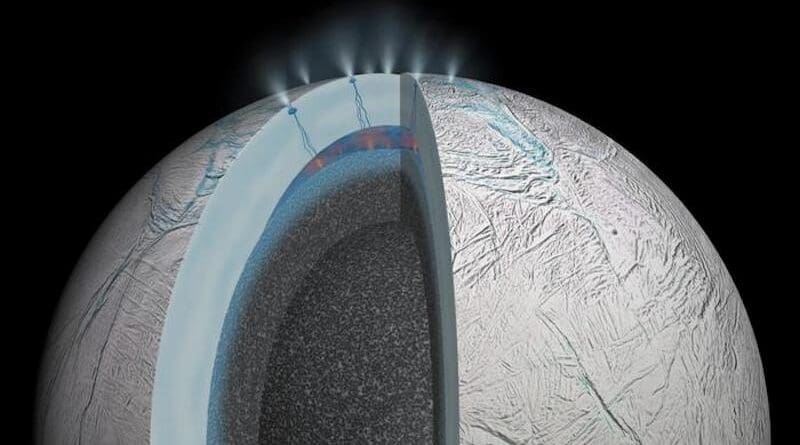
Signs in the Ice: Detectable Biosignatures in Tiny Samples
The recent study led by Fabian Klenner, a planetary scientist at the University of Washington, proposes a revolutionary approach. The research team posits that biosignatures – chemical or isotopic signatures indicative of biological activity – could be detectable even in a single grain of ice ejected from these moons. This opens up a new avenue for upcoming space missions like Europa Clipper and JUICE, designed to explore these distant worlds.
Simulating the Cosmos: Recreating Icy Grains in the Lab
To test their hypothesis, the researchers devised a clever experiment that simulated icy grains in space. They used the single-celled bacterium S. alaskensis, known for its resilience in frigid environments, as a model for potential extraterrestrial life. The bacterium was introduced into a liquid water solution, which was then subjected to a vacuum environment to mimic the conditions of space. Sophisticated techniques like laser ablation and spectral analysis were employed to determine if the cellular material remained detectable after being frozen and subjected to the harsh vacuum.
The results of the experiment were highly encouraging. The researchers successfully identified the presence of the bacterium, and even fragments of it, within the simulated ice grains. This finding significantly bolsters optimism that similar techniques could be applied to analyze real extraterrestrial material, potentially revealing biosignatures from distant worlds.
Missions on the Horizon: Unveiling the Secrets of Icy Moons
The upcoming Europa Clipper and JUICE missions add another layer of excitement to this scientific endeavor. Europa Clipper, scheduled to arrive at Jupiter in 2030, will be equipped with the SUrface Dust Analyzer (SUDA). This powerful instrument is designed to detect cellular material in a single ice grain amidst a plume of ejected material from Europa.
The findings of the recent study, coupled with the capabilities of these upcoming missions, paint an optimistic picture. The icy plumes erupting from these moons can be seen as celestial messengers, carrying traces of their hidden oceans to us. Analyzing these plumes, and the individual ice grains within them, could be the key to unlocking the secrets of extraterrestrial life. Future missions might even discover a form of “seafoam,” similar to that found on Earth, floating on the surface of these alien oceans. Such a scenario could make biosignatures even easier to detect, as these materials get ejected into space.
The wait for Europa Clipper’s arrival in 2030 may seem long, but these advancements serve to heighten the anticipation. With each passing day, the prospect of unraveling the mysteries of life beyond Earth seems to inch closer. The icy moons of Jupiter and Saturn beckon, holding the potential to rewrite our understanding of the universe and our place within it. As we stand poised on the precipice of this groundbreaking scientific endeavor, the possibility of detecting life in a single grain of ice from a distant world ignites our imagination and fuels our collective pursuit of knowledge about the existence of life beyond our pale blue dot.


















