Astronomers have unearthed a fascinating connection between a recently discovered black hole and a neighboring disrupted star cluster. This discovery, detailed in a new study published on the preprint server arXiv, sheds light on the origins of both the black hole and the scattered cluster, offering a glimpse into the violent past of our galaxy.
A Heavyweight in the Stellar Neighborhood: Unveiling Gaia BH3
The newfound black hole, designated Gaia BH3, resides a mere 1,900 light-years away within our Milky Way galaxy. Classified as a stellar-mass black hole, Gaia BH3 boasts an impressive mass of 33 solar masses, making it the most massive black hole of its kind ever discovered in our cosmic backyard. Interestingly, Gaia BH3 isn’t alone; it shares a gravitational dance with a companion – an old, metal-poor giant star roughly five times larger than our Sun.
A Scattered Past: ED-2, the Disrupted Star Cluster
The intriguing twist comes with the discovery that Gaia BH3 is intricately linked to a disrupted star cluster known as ED-2. Once a tightly bound group of stars, ED-2 has been ravaged by the gravitational forces within our galaxy, scattering its stellar inhabitants across the galactic halo like celestial shrapnel. This faint trail of stars, known as a stellar stream, is called ED-2 and is estimated to be composed of stars with a low metal content, similar to the companion star of Gaia BH3.
Chemical Fingerprints Tell the Tale: Connecting the Dots
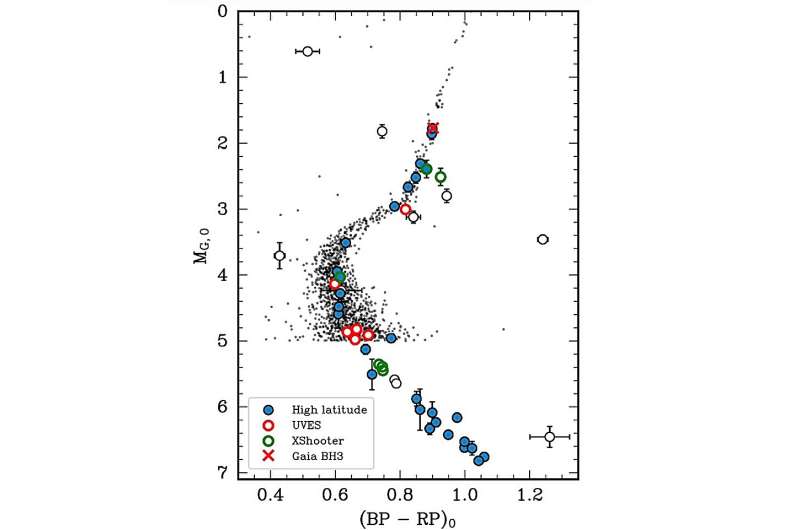
A meticulous analysis of the chemical makeup of both the stars within ED-2 and the giant star companion of Gaia BH3 revealed a remarkable similarity. This chemical fingerprint, which includes the abundance of elements like magnesium and europium, serves as a unique identifier, strongly suggesting that both the black hole and its companion originated from the same stellar nursery – the now-disrupted ED-2 cluster.
Orbital Lockstep: A Shared Journey Through Time
The investigation didn’t stop there. Astronomers compared the orbital trajectory of Gaia BH3 around the Milky Way galaxy with the paths traced by stars confirmed to be members of ED-2. The results were striking – the orbits were practically indistinguishable. This remarkable alignment further strengthens the case for a shared origin between the black hole and the disrupted cluster.
Peering into the Past: Unveiling the Formation of a Stellar Heavyweight
The newfound connection between Gaia BH3 and ED-2 allows astronomers to piece together a narrative of their formation. The data suggests that the progenitor star that birthed Gaia BH3 likely formed over 13 billion years ago, a mere few billion years after the Big Bang. The environment within the nascent ED-2 cluster may have played a crucial role, with the possibility of the black hole forming either from the direct collapse of a massive star or through a complex interplay of binary interactions within the dense cluster.
A Window into a Violent Past: Unveiling the Secrets of Stellar Evolution
This discovery not only unveils the origins of a captivating black hole, but also offers valuable insights into the tumultuous past of our galaxy. The disruption of star clusters like ED-2 likely played a significant role in shaping the Milky Way’s structure and distribution of stars. Imagine a time when our galaxy was a far more turbulent environment, with young star clusters constantly forming, interacting, and occasionally being ripped apart by powerful gravitational forces. These disruptions would have scattered stars throughout the galaxy, enriching different regions with unique chemical signatures. By studying these stellar streams and their associated black holes, astronomers can begin to reconstruct this chaotic chapter in our galaxy’s history.
A Beacon for Future Discoveries: Unveiling the Landscape of Black Holes
The discovery of Gaia BH3 also holds significance for our understanding of black holes in general. Stellar-mass black holes, formed from the collapse of massive stars, are elusive denizens of our galaxy. They are difficult to detect directly due to their lack of light emission. However, the presence of a stellar companion, as in the case of Gaia BH3, can betray the black hole’s presence through the gravitational dance they share. Future studies of Gaia BH3 and similar systems can provide valuable insights into the formation and evolution of stellar-mass black holes, helping us to refine our understanding of these enigmatic objects.
This ongoing quest to unravel the mysteries of black holes and stellar evolution is far from over. The discovery of Gaia BH3 and its connection to ED-2 serves as a testament to the power of astronomical investigation. By meticulously piecing together the chemical fingerprints and orbital histories of celestial objects, astronomers can unveil the grand narrative of our galaxy’s formation and evolution, bringing us ever closer to understanding our place in the vast cosmic ocean.


















