A recent study published in the journal Science has reignited interest in Jupiter’s moon Io, revealing evidence that suggests Io’s volcanic activity has been a constant presence for a staggering 4.5 billion years – practically since the birth of our solar system!
This finding, led by a team of researchers from the California Institute of Technology, the University of California Santa Cruz, New York University, and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, sheds new light on the moon’s long and fiery history.
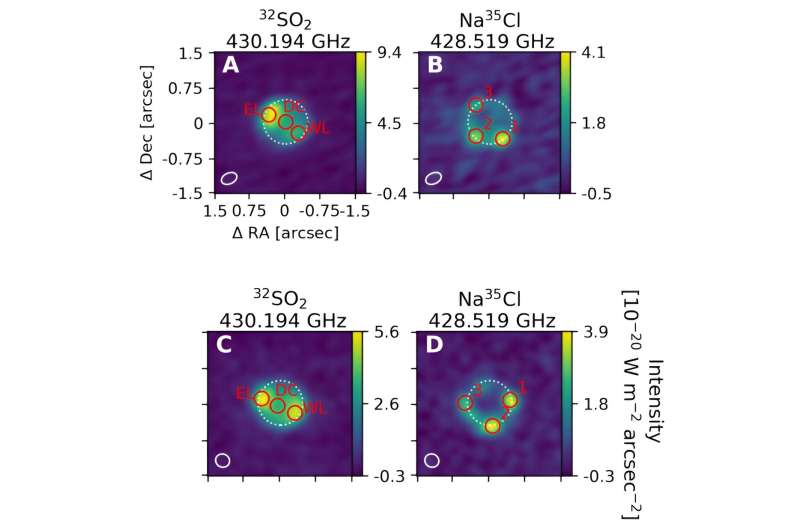
Prior research had already established Io as the most volcanically active body in our solar system. Volcanic plumes erupt hundreds of kilometers from Io’s surface, dwarfing even the most explosive volcanoes found on Earth. However, the exact duration of this activity remained a mystery. To address this, the research team turned to the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), a powerful telescope that can analyze the faint light emitted by gasses present in Io’s thin atmosphere.
The Perpetual Dance of Fire and Gravity
The relentless volcanic eruptions on Io are a consequence of the immense gravitational pull it experiences. Jupiter, along with Io’s neighboring moons, Ganymede and Europa, exert a tug-of-war effect on Io.
This constant wrestling match generates immense frictional heating within Io’s interior, leading to the molten rock fountains that erupt onto its surface. Unlike Earth, where plate tectonics play a major role in volcanic activity, Io’s volcanoes are a direct result of these tidal forces.
The pull and squeeze from Jupiter and its neighboring moons literally stretch and compress Io’s internal structure, like a giant celestial hand repeatedly squeezing a stress ball. This continual flexing creates friction, heating the moon’s core and fueling the volcanic eruptions.
Unearthing Io’s Secrets Through its Atmosphere
The researchers focused on two key pieces of evidence within Io’s atmosphere: chlorine molecules and the isotopic ratios of sulfur. When compared to other celestial bodies, Io’s atmosphere exhibited a much higher abundance of both elements. Additionally, the study revealed that a significant portion (between 94% and 96%) of the sulfur released by volcanic eruptions escapes Io’s atmosphere and is lost to space.
This unique combination of factors – the presence of specific elements and the high rate of atmospheric loss – strongly suggests that Io’s volcanic activity has been a constant geological process for its entire existence. The relentless volcanic eruptions have continuously reshaped Io’s surface, burying any potential record of a past geological era. This makes it challenging for scientists to directly study Io’s history through traditional geological methods used on other celestial bodies.
A Glimpse into a Fiery Past
However, the research team is not discouraged. Future studies will focus on utilizing the data gathered from Io’s atmosphere to investigate whether the moon had an initial period with a cooler surface and a potentially different geological makeup.
The presence of specific elements like chlorine may provide clues about the existence of an ancient ice crust or even a subsurface ocean that may have been vaporized by the relentless volcanic activity over billions of years. These investigations will undoubtedly provide a more comprehensive picture of this fascinating volcanic moon and its place within our solar system. Io may be a world constantly in flux, but through the analysis of its atmosphere, scientists hope to unravel the secrets it holds about its fiery past.
By studying the unique composition of Io’s atmosphere and the rate at which atmospheric elements escape, scientists can potentially reconstruct a timeline of volcanic activity. The presence of certain elements may indicate the types of materials that were once present on Io’s surface before being vaporized or ejected by volcanic eruptions.
These clues, along with data from future space missions, could help paint a more complete picture of Io’s evolution and uncover the secrets of this perpetually active and enigmatic moon.


















