The birth of stars is a far cry from the serene image we often imagine. It’s a dynamic and disorderly process, particularly in its early stages. Complex gas structures, swirling in the form of spirals and streamers, characterize this period. These formations, known as “feeding filaments,” act like cosmic umbilical cords, funneling surrounding gas toward the newborn star.
The Brown Dwarf Enigma
Brown dwarfs, celestial objects with masses less than one-tenth of our Sun, are too small to ignite nuclear fusion and shine like stars. Scientists have been puzzled by the question of whether brown dwarfs form in a similar way to stars, or if there’s a distinct process at play.
High-Tech Observations Shed Light
Previously, a lack of high-resolution data during a brown dwarf’s earliest formation stages hindered scientific understanding. An international team led by Dr. Basmah Riaz (LMU astrophysicist) has addressed this gap through observations of the young brown dwarf Ser-emb 16 using the powerful ALMA observatory in Chile. Their findings have been published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Spectacular Structures Revealed
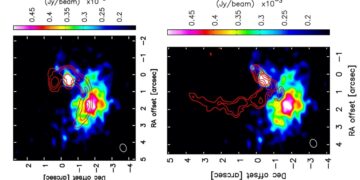
“Our observations have revealed never-before-seen, large-scale spiral and streamer structures surrounding a newly forming brown dwarf,” explains Dr. Riaz. These vast filaments, spanning 2,000-3,000 astronomical units, connect directly to Ser-emb 16. Additionally, clumps of material were observed nearby, potentially evolving into young brown dwarfs themselves.
The Role of the Environment
These observations offer the first-ever glimpse into how the external environment influences brown dwarf formation. “They show, for the first time, the influence of the external environment, which results in asymmetric mass accretion via feeding filaments on to a brown dwarf in the making,” says Dr. Riaz. The data suggests an “asymmetric mass accretion” process, where feeding filaments deliver material unevenly to the developing brown dwarf.
Competing Theories: Collapsing Clumps or Magnetic Influence?
The observed spirals and streamers provide valuable clues about brown dwarf formation. Researchers compared simulated scenarios with the ALMA data. One explanation involves collisions between collapsing clumps within a star-forming region. Co-author Dr. Dimitris Stamatellos (University of Central Lancashire) suggests that such collisions if occurring sideways, could create the large-scale structures observed. This scenario implies a dynamic formation process for brown dwarfs, similar to stars, where chaotic interactions are prevalent from the beginning.

Prof. Albert Zijlstra, Jodrell Bank Professor of Astrophysics
An alternative scenario suggests that the observed structures represent a twisted “pseudo-disk” surrounding the young brown dwarf. This model proposes that a strong magnetic field within the brown dwarf core twists the disk. If this scenario holds true, then magnetic fields play a significant role in brown dwarf formation.
A Star-Like Birth for Ser-emb 16?
“Our ALMA observations offer a unique window into the early formation stages of brown dwarfs,” says Dr. Riaz. Comparisons between the observations and models favor a gravitational infall scenario, similar to star formation. This explains the asymmetric mass accretion evident in the spirals and streamers.
“Consequently,” explains co-author Professor Masahiro Machida (Kyushu University), “Ser-emb 16 emerges as a unique case, captured in the act of forming in a star-like fashion.” This suggests that brown dwarfs may not be so different from their larger stellar cousins after all, at least in their early stages of development.
These new findings provide significant insights into the formation of brown dwarfs, objects that have long puzzled astronomers. Future studies, building on Dr. Riaz’s team’s work, will likely shed more light on the various factors that influence the birth of these celestial bodies and how they diverge from the well-understood process of star formation.