In the age of ubiquitous high-resolution cameras, a recent space mission might seem like a step backward. The newly launched XRISM satellite, a collaborative effort between NASA and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), boasts an instrument unlike any other – Resolve, a sensor with a mere 36 pixels. Don’t be fooled by the low pixel count, though! Resolve represents a revolutionary leap forward in the study of X-ray emissions from the cosmos.
Quality Over Quantity: Unveiling the Universe’s Secrets
While our smartphones might hold cameras boasting megapixels in the hundreds of millions, XRISM’s Resolve takes a different approach. This innovative sensor prioritizes quality over sheer quantity. Each of its 36 pixels is a powerhouse, meticulously designed to measure the temperature of X-ray emissions with exceptional precision. Think of it as a microscopic thermometer, gauging the scorching heat of distant celestial objects, but with an added layer of sophistication. By meticulously analyzing the energy signature of each X-ray, Resolve can not only measure temperature, but also delve into the makeup of the object that emitted it. This spectral analysis unlocks a treasure trove of information, akin to a celestial fingerprint, revealing the elemental composition of the object and its current state.
Resolve: The Heart of XRISM
Launched in September 2023, XRISM carries Resolve as its crown jewel. While details surrounding the mission have been scarce, recent revelations from NASA shed light on this groundbreaking instrument. Resolve’s sensor is a 6×6 grid of surprisingly large pixels, each one a testament to its focus on high-fidelity data collection. Unlike traditional cameras that capture an image by recording the intensity of light across an array of pixels, Resolve’s strength lies in its ability to measure the energy of individual X-ray photons with unmatched precision. Imagine a symphony of light being reduced to the delicate dance of individual notes – Resolve offers a similar level of detail, dissecting the X-ray spectrum to reveal the true nature of its source.
Beyond Imaging: A Spectroscopic Marvel
Resolve transcends the limitations of a traditional camera. Brian Williams, NASA’s XRISM project scientist, aptly describes it as “more than a camera.” Each pixel functions as a miniature “microcalorimeter spectrometer,” independently analyzing the heat signature of incoming X-rays. This remarkable precision allows scientists to not only detect X-rays but also decipher a wealth of information. By meticulously examining the X-ray spectrum, they can determine the composition of the celestial object that emitted the energy, along with its motion within the vast expanse of space. Imagine a single pixel with such capabilities – Resolve boasts an impressive 36, forming a powerful scientific instrument akin to a celestial detective kit, dissecting the properties of distant objects with unparalleled precision.
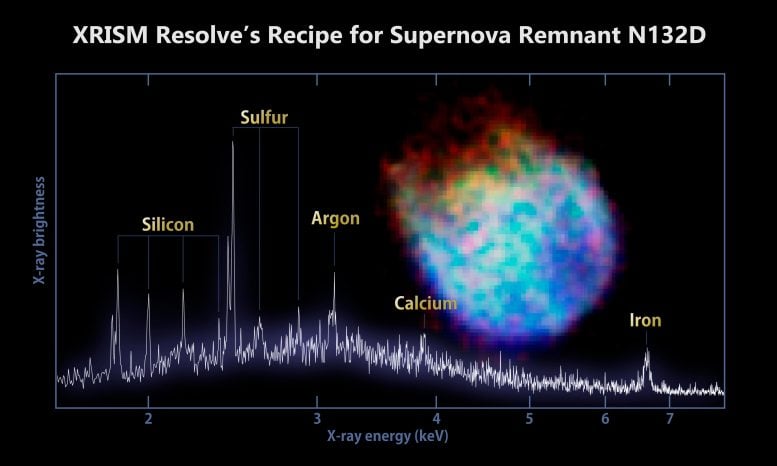
Unlocking the Universe’s Secrets: From Black Holes to Superheated Gas
XRISM, with Resolve at its core, will train its gaze on some of the universe’s most captivating phenomena. Supermassive black holes, the enigmatic remnants of exploded stars known as supernovae, and the scorching gas clouds within galaxy clusters – all will be unveiled with unprecedented clarity through the lens of X-ray spectroscopy. Resolve’s ability to measure the energy and composition of X-ray emissions will provide scientists with a deeper understanding of these celestial giants. For instance, studying the X-ray signature of a black hole’s accretion disk can shed light on its feeding behavior and the immense gravitational forces at play. Similarly, analyzing the X-ray spectrum of a supernova remnant can reveal the elements forged in the fiery explosion, enriching our understanding of stellar evolution and the elements that make up our universe.
A Stepping Stone to the Future
While details about XRISM’s findings have been limited thus far, the mission is designed for a two-and-a-half-year exploration. The potential for future advancements is equally exciting. NASA envisions this mission as a stepping stone towards even more powerful instruments, with microcalorimeter pixel arrays numbering in the hundreds or even thousands. Imagine a future where telescopes like XRISM are commonplace, carrying out detailed X-ray spectroscopic investigations of distant galaxies and unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos in ways we can only begin to imagine.
A Testament to Innovation: Pushing the Boundaries of Exploration
Despite the initial setback of a malfunctioning shutter limiting Resolve’s observable energy range, the information it gathers is invaluable. This mission serves as a testament to NASA’s unwavering commitment to innovation. With Resolve leading the charge, a new era of X-ray space exploration has begun, promising to unveil the universe’s secrets in ways never before imagined. As XRISM continues its cosmic survey, we stand at the precipice of a profound shift in our understanding of the cosmos. With Resolve’s groundbreaking capabilities, we are poised to delve deeper into the mysteries of the universe, unraveling its intricacies one X-ray at a time. As XRISM continues its cosmic survey, we stand at the precipice of a new era in space exploration, where the boundaries of what we can discover are limited only by the bounds of our imagination.
In conclusion, as XRISM, with its revolutionary Resolve instrument, embarks on its mission to explore the cosmos, it not only represents a triumph of scientific innovation but also a beacon of hope for humanity’s quest to understand the universe. With each pixel of Resolve serving as a gateway to unlocking the secrets of distant celestial objects, we are on the verge of unprecedented discoveries that will reshape our understanding of space and time. As we gaze into the depths of the cosmos, let us remember that it is not merely the pixels that define our journey, but the boundless curiosity and determination of the human spirit that propel us ever closer to the stars.
















